Are you ready to find 'sucrose synthesis'? You can find questions and answers on the topic here.
Table of contents
- Sucrose synthesis in 2021
- Hydrolysis of sucrose
- Sucrose synthesis in plants
- Metabolism and regulation of sucrose in plants
- Function of sucrose in plants
- Sweet transporter
- Synthesis of sucrose reaction
- Sucrose synthase enzyme
Sucrose synthesis in 2021
 This image illustrates sucrose synthesis.
This image illustrates sucrose synthesis.
Hydrolysis of sucrose
 This picture shows Hydrolysis of sucrose.
This picture shows Hydrolysis of sucrose.
Sucrose synthesis in plants
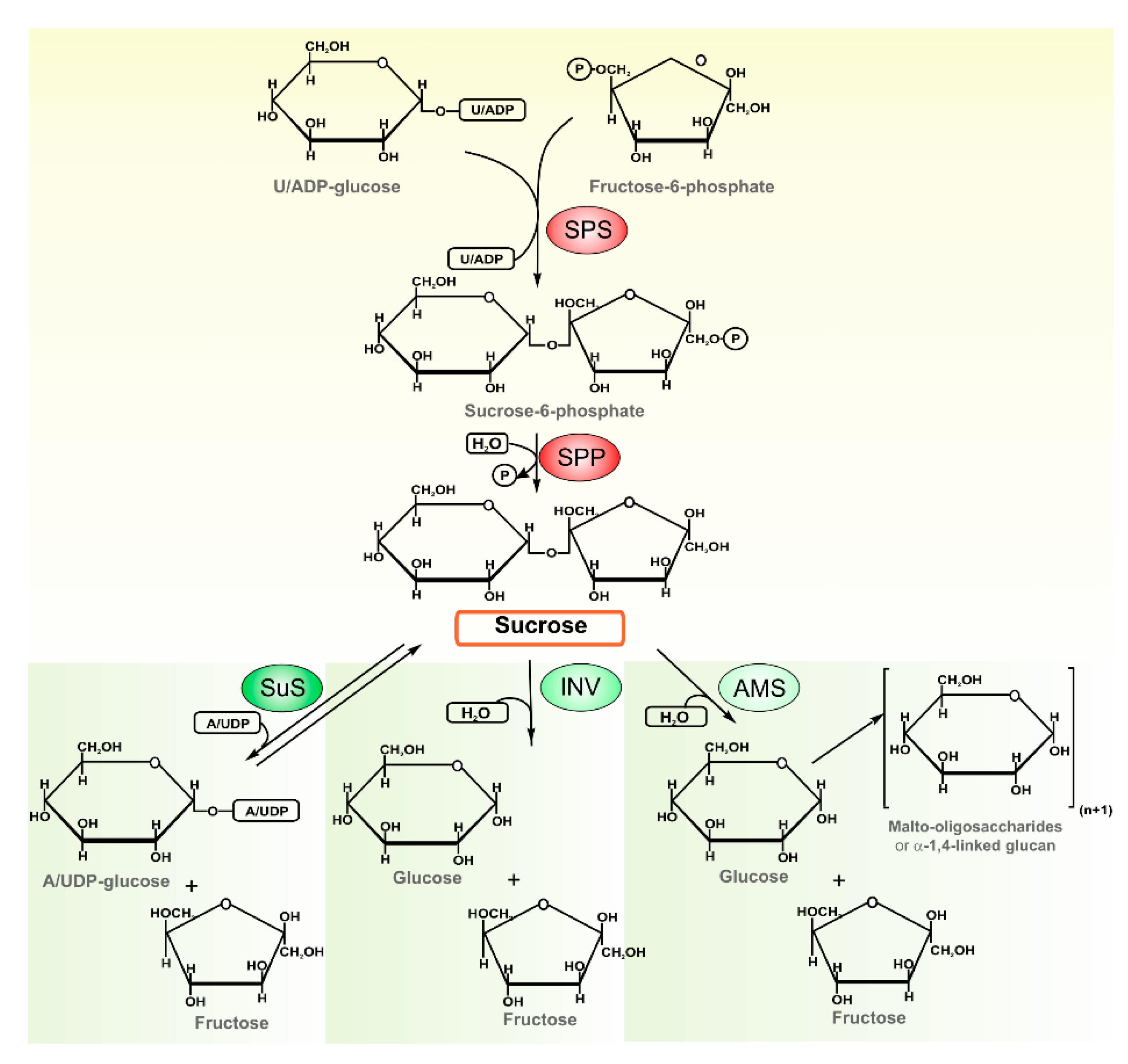 This picture shows Sucrose synthesis in plants.
This picture shows Sucrose synthesis in plants.
Metabolism and regulation of sucrose in plants
 This picture shows Metabolism and regulation of sucrose in plants.
This picture shows Metabolism and regulation of sucrose in plants.
Function of sucrose in plants
 This image representes Function of sucrose in plants.
This image representes Function of sucrose in plants.
Sweet transporter
 This picture shows Sweet transporter.
This picture shows Sweet transporter.
Synthesis of sucrose reaction
 This image illustrates Synthesis of sucrose reaction.
This image illustrates Synthesis of sucrose reaction.
Sucrose synthase enzyme
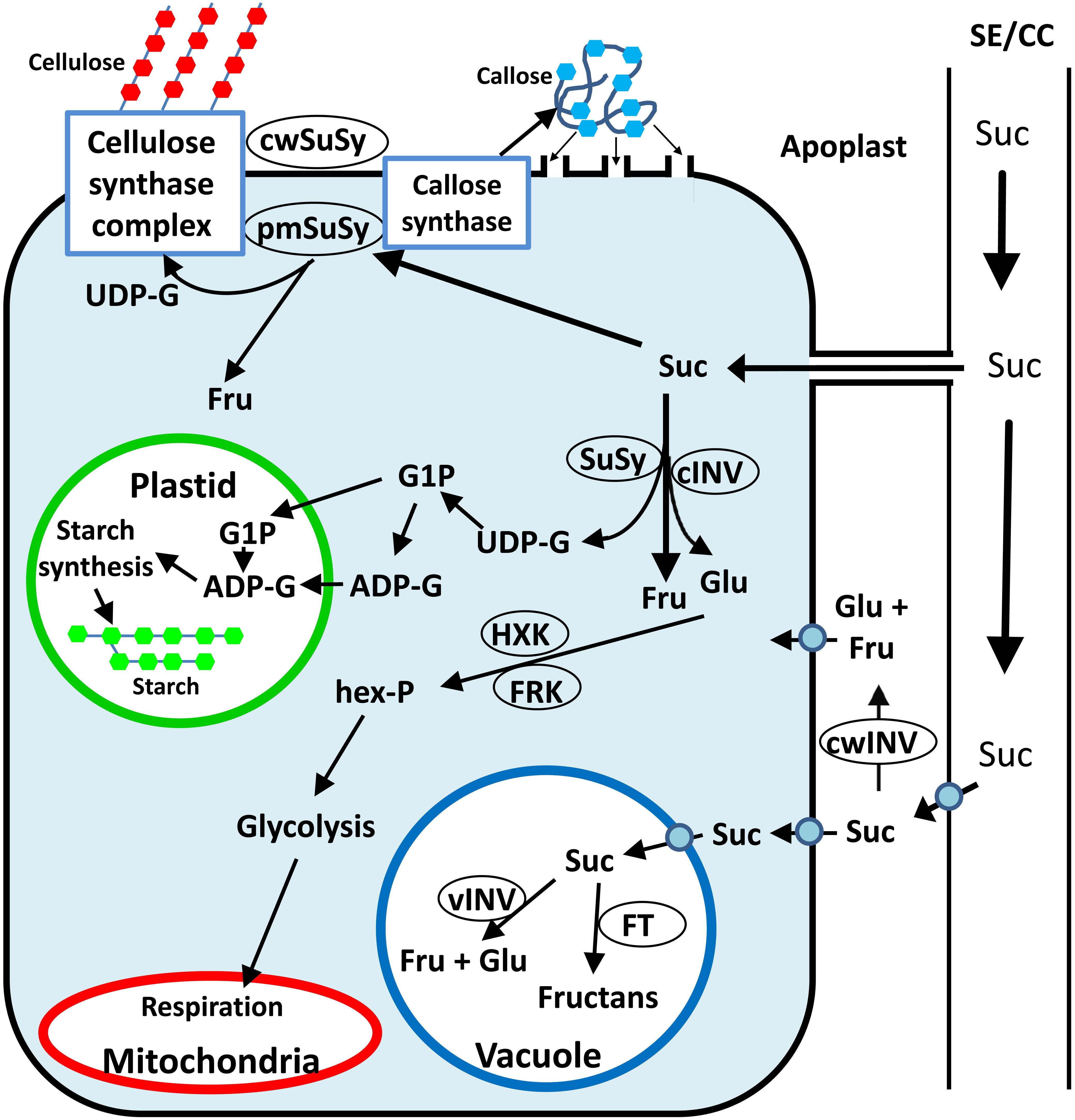 This image illustrates Sucrose synthase enzyme.
This image illustrates Sucrose synthase enzyme.
Where does the synthesis of sucrose take place?
Synthesis of sucrose in plants may take place by 3 different ways: (1) From Glucose-1-Phosphate and Fructose in the presence of the enzyme sucrose phosphorylase e.g., in bacteria. (2) From UDPG (Uridine Di-Phosphate Glucose) and Fructose in the presence of the enzyme sucrose synthetase e.g., in higher plants.
How is sucrose broken down into glucose and fructose?
Cellulose in Plants. Sucrose is broken down or hydrolysed to yield glucose and fructose in the presence of the enzyme invertase or sucrase. The reaction is irreversible. Synthesis of sucrose in plants may take place by 3 different ways: (1) From Glucose-1-Phosphate and Fructose in the presence of the enzyme sucrose phosphorylase e.g., in bacteria.
How is the sucrose-6-acetate intermediate produced?
The sucrose-6-acetate intermediate is produced by selective acetylation of sucrose. A detailed synthetic scheme follows. First, sucrose is selectively protected at the glucose C6 by an acetyl group, to sucrose-6-acetate ( 5 ).
What is the role of sucrose synthase in the sink?
Sucrose synthase (SuSy) is a glycosyl transferase enzyme that plays a key role in sugar metabolism, primarily in sink tissues. SuSy catalyzes the reversible cleavage of sucrose into fructose and either uridine diphosphate glucose (UDP-G) or adenosine diphosphate glucose (ADP-G).
Last Update: Oct 2021